vagrant rancher2.0 kubernetes orchestration tool example
This example shows a rancher2.0 server and kubernetes worker servers based on a docker environment on top of a VM-based vagrant local(OSX/Windows) environment..
Rancher[1] is an well known attractive tool for orchestrating containers in a docker environment.
Rancher ver1.6 uses swarm-based cattle engine, kubernetes, mesos, etc., while ver2.0 supports only kubernetes engine and is under full reorganization.
There is a way to develop a docker application locally by configuring a container environment pool based on the vagrant VM.[2]
if use OSX and use rb, this is better example.[3].
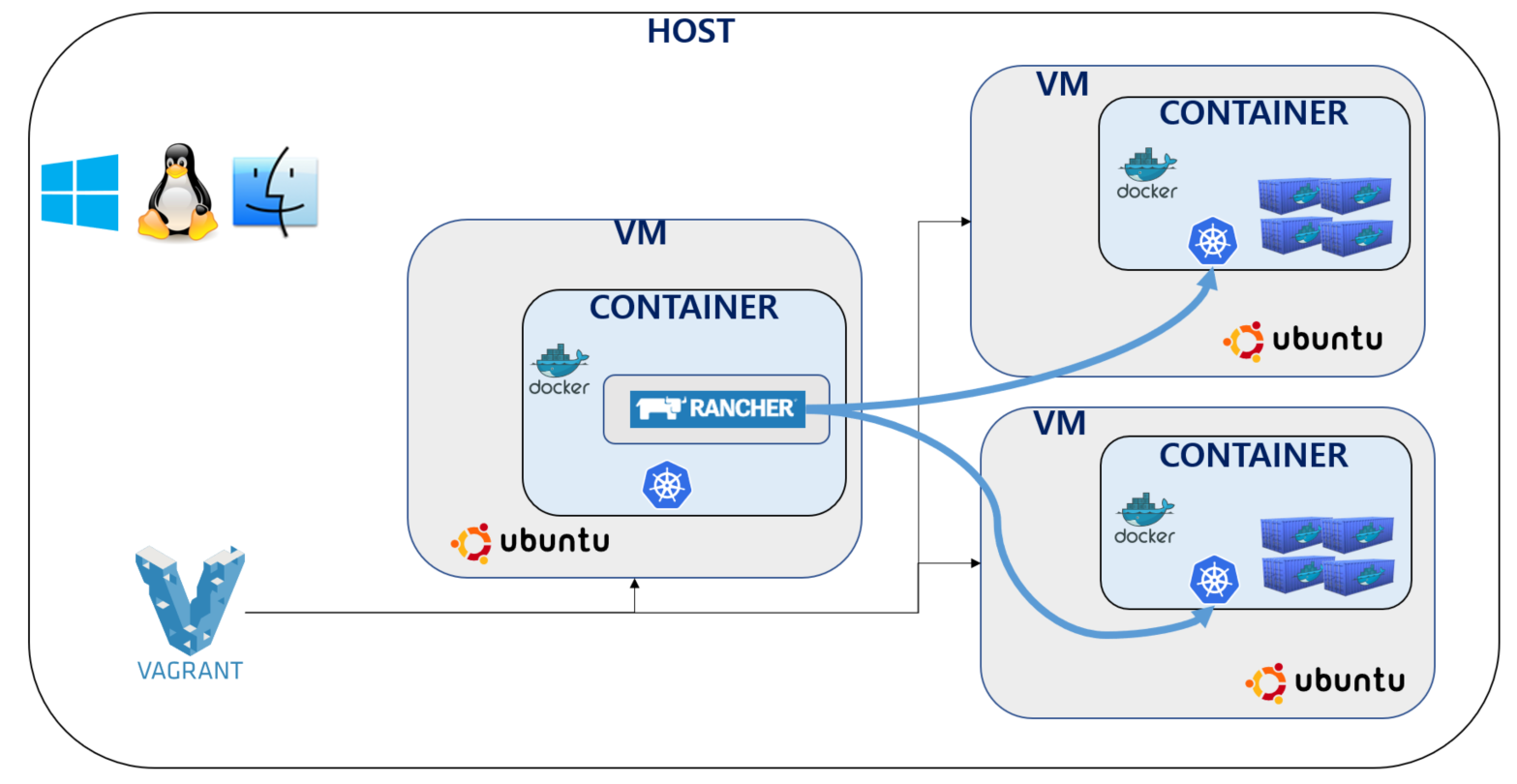
Install Vagrant and Virtual Box in your local(OSX/Windows) environment.
Vagrant is required as this is used to provision the machine based on the Vagrantfile.
The virtual machines that Vagrant provisions need to be provisioned to VirtualBox.
git clone https://github.com/hyeonsangjeon/vagrant-rancher2.0.git
cd vagrant-rancher2.0vagrant up rancher
cd vagrant-rancher2.0vagrant up vmhost01vagrant up vmhost01 && vmhost02
| info | Description | ssh |
|---|---|---|
Rancher server |
https://192.200.10.100 |
22 |
K8S Worker servers |
192.200.10.1x |
22 |
| info | Description |
|---|---|
vagrant up |
This command creates and configures guest machines according to your Vagrantfile.[4] |
vagrant destroy |
This command stops the running machine Vagrant is managing and destroys all resources that were created during the machine creation process. |
vagrant ssh |
This will SSH into a running Vagrant machine and give you access to a shell. |
cd vagrant-rancher2.0vagrant ssh ranchervagrant ssh vmhost01vagrant ssh vmhost0x
how_to_use shows simple example rancher2.0 ui
[1].https://rancher.com/ [2].https://github.com/goody80/vagrant_rancher_cluster [3].https://rancher.com/docs/rancher/v2.x/en/quick-start-guide/deployment/quickstart-vagrant/[4].https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/cli/up.html[5].https://objectcomputing.com/resources/publications/sett/march-2015-docker-vs-vagrant